
Industrial Automation: Connecting Operations, People, Machines
By:
OMA
|
2024-July-5
Bringing Real-Time to the Masses
The future of innovative industrial and manufacturing sectors is driven around industry 4.0, real-time production and industrial insights, machine learning, robotics, and agile practices. The industrial and manufacturing sectors are undergoing a revolutionary transformation, driven by cutting-edge innovations that are reshaping traditional processes and boosting efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.Understanding the industrial ecosystem can be impactful for engineering, integration, installation, and servicing customers in industries such as manufacturing, energy production, waste management, utilities, and others. Below is a depiction of the manufacturing ecosystem:

Here’s a glimpse into some of the 3 most impactful advancements making waves in these industries.
- Smart Manufacturing: Industry 4.0 & Agile Production Industry 4.0 has been at the center of manufacturing automation, mass customization, and digital transformation for the past 5 years. This involves the integration of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and the use of software and systems to digitize manufacturing processes and operations. Smart factories equipped with connected machinery (pick and place, sorting, tagging, production, etc.) and advanced sensors collect vast amounts of data in real time. This data is then analyzed to optimize production processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve product quality. The result is a more agile, efficient, and responsive manufacturing environment. Smart manufacturing encompasses new and innovative approaches to take raw material and make into a final product that is less costly, more efficient, high quality, and produced in a more “on-demand” fashion. Below are some real-world examples of how Industry 4.0 is being used by companies:
- Siemens’ Amberg Electronics Plant in Germany exemplifies a smart factory. Utilizing IoT devices, sensors, and real-time data analytics, the plant has achieved near-perfect production quality and significant efficiency improvements. Autonomous robots and AI-driven systems handle complex tasks, reducing human error and enhancing productivity.
- BMW leverages AI and machine learning in its production lines to optimize manufacturing processes. AI systems predict equipment failures and maintenance needs, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of production data to identify patterns and improve quality control.
- Caterpillar uses predictive maintenance solutions across its heavy machinery and equipment. By analyzing data from sensors embedded in their machinery, Caterpillar can predict when a component is likely to fail and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
- Automation: IoT, AI, Machine Learning & Robotics Internet of things (IoT) has been part of the industrial and manufacturing sectors for almost a decade, and in fact we embraced machine-to-machine (M2M) technologies before we started calling it IoT. Connecting machines, assets (human and equipment), and systems was just the beginning. We are now moving into taking the intelligence of these “connected” cyber-physical environments and acting, predicting, alerting, and responding in near real-time. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing pivotal roles in enhancing decision-making processes across the manufacturing sector. AI-powered systems can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and insights that human analysis might miss. Machine learning algorithms improve predictive maintenance, optimize supply chain logistics, and enhance quality control, leading to reduced downtime and operational costs. The adoption of robotics and automation is accelerating, with robots taking on increasingly complex tasks. Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside human workers to enhance productivity and safety. Automation is streamlining repetitive and hazardous tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of manufacturing. This synergy between human and machine is paving the way for more efficient and flexible production processes. Below are a few examples where companies are using automation technology in action:
- Nestlé uses robotic systems for packaging and palletizing in its factories. Robots help in automating repetitive tasks such as sorting, packaging, and stacking products, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing human labor costs.
- Adidas has introduced robotic systems in its Speedfactory to automate the production of shoes. Robots are used for knitting, cutting, and assembling shoe components, allowing for customized production and faster turnaround times.
- Rio Tinto uses autonomous haul trucks and drilling systems in its mining operations. These robotic systems can operate continuously and are controlled remotely, improving safety and efficiency in harsh mining environments.
- AMP Robotics uses AI-powered robots to sort recyclable materials in waste management facilities. These robots can identify and separate different types of materials with high accuracy, improving the efficiency of recycling processes.
- Digital Simulation: Digital Twins & Prototype Learning A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, system, or process. It is used to simulate, predict, and optimize performance in real-time, leveraging data from sensors and IoT devices. Digital twins are revolutionizing how manufacturers design, monitor, and maintain their products and systems. By simulating real-world conditions, digital twins enable manufacturers and industrial sectors to test and optimize products, processes, supply chains, and test outcomes in a virtual environment before implementation. This reduces the risk of errors, lowers costs, and speeds up the innovation cycle. Rolls-Royce, for example, uses digital twin technology to create virtual models of their jet engines. These digital twins simulate real-world conditions, allowing engineers to predict performance, identify potential issues, and optimize maintenance schedules without physical intervention. Below are examples of how digital twin technology can be used in manufacturing:
- Prototype Testing: Before physical prototypes are built, manufacturers can create digital twins of new products to test their designs. This allows engineers to simulate how a product will perform under various conditions and make necessary adjustments to the design.
- Stress and Performance Testing: Digital twins enable the simulation of stress tests, thermal tests, and other performance-related scenarios. By analyzing how the virtual product reacts, manufacturers can predict potential issues and improve the design to enhance durability and functionality.
- Production Line Simulation: Manufacturers can create digital twins of entire production lines to simulate different production scenarios. This helps in identifying bottlenecks, optimizing workflows, and testing the impact of changes without disrupting actual production.
- Testing Quality Assurance Processes: Manufacturers can simulate different quality assurance protocols to determine which methods are most effective in catching defects and ensuring high product standards.
Industry Innovation Wrap Up
As we push processes, supply chains, logistics, and delivery of goods and services into a more mobile and on-demand manner, wired infrastructure and Wi-Fi does not deliver. Reliable, secure, and seamless connectivity is at the foundation of these innovative technologies being used to transform the industrial sector. As 5G gets “turned on” there is also a driving trend of using private wireless, edge computing, machine learning, large language models, and data analytics for critical applications that require a higher level of privacy, security, and control. As we continue to digitally transform the industrial and manufacturing sectors, we push further into open development, automated processes, robotics, telematics, and the ability for action in near real-time as we connect people, machines, assets, and fleets.
The Digital Transformation of Manufacturing/Industrial, From 2004 to 2024
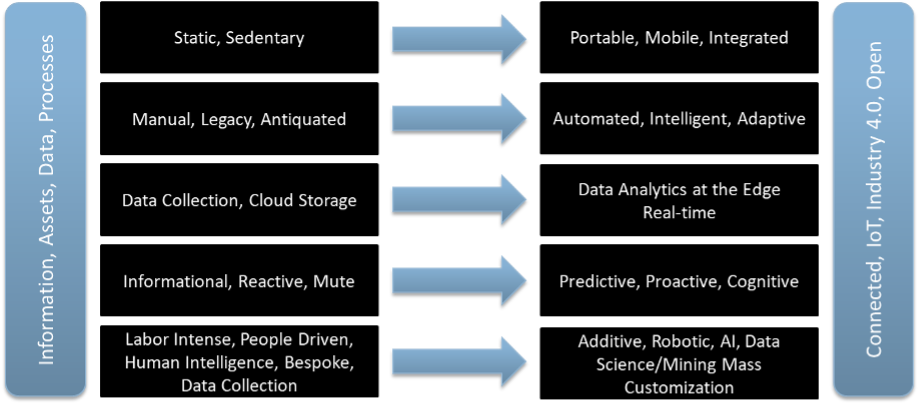
Source: CompassIntel.com, 2024.
The industrial and manufacturing sectors are experiencing a dynamic shift, driven by these groundbreaking innovations. As technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are better equipped to meet the demands of a fast-paced, ever-changing market. The on-demand economy is driving the need for faster and more efficient production delivered to the customer. Embracing these advancements not only enhances operational efficiency and product quality but also sets the stage for a more sustainable and resilient industrial future. The journey towards a smarter, more innovative manufacturing landscape is well underway, promising exciting developments in the years to come.
